What Does It Mean When It Say Defective Battery?
There are several ways for battery testing. Let’s start with the beginning. First gives you a basic idea about battery defects. The defects that occur in batteries can usefully be classified as either of a mechanical or chemical nature.
Mechanical defects include cracked or bulged cases, loose sealing compounds, buckled plates, charred or cracked separators, cracks in partitions, broken plate straps or grids, damaged terminal posts and faulty inter-cell links.
Chemical defects include excessive evaporation of water, loss of electrolyte, gassing and boiling over, sulphation, plate shedding, and, in extreme temperatures, electrolyte freezing.
What Are the Main Cause of Battery Troubles?
The main causes of battery troubles are.
- Undercharging.
- Overcharging.
- Lack of water.
- Standing in a discharged condition.
- Old age results in loss of capacity.
- Corrosion.
- Acid spilling.
- Mechanical troubles.
- The excessive load on the battery.
- Loose holding-down bolts.
- Defective cables and
- improper cable size.
What Causes Battery Undercharging?
- The main causes of undercharging are.
- Too frequent use of the starter.
- Leaving the vehicle for long periods with lights on.
- Leaving ignition or accessories switched on.
- Low setting of the voltage regulator, or
- Any condition which results in more current being taken out of the battery than is put into it.
A major cause of undercharging is sulphation which, if excessive, will set up strains causing the battery plates to distort.
What Causes Battery Overcharging?
On modern vehicles, the main cause of overcharging is the setting of the voltage regulator. But any condition which results in a lack of balance between the energy sent into the battery and that taken from it will result in overcharging. The consequences of overcharging include disintegration of plate active material, excessive gassing, rapid evaporation, unduly strong electrolyte, which will harm the separators and battery plates, and high internal heating which may damage the plates and separators.
Lack of Water-What Happens If Electrolytes Are Low in Battery?
An important need in battery servicing is the periodic adjustment of electrolytes lost through evaporation. This is needed whenever the electrolyte level falls to the top of the separators. If the evaporated water is not replaced the electrolyte will become too strong and damage to the separators and plates will result.
Should I Disconnect Car Battery When Standing Idle?
Batteries should not be allowed to stand in a discharged condition for a long period. Otherwise, they will become sulfated and develop the troubles outlined under the heading “ undercharging”.
What Causes Battery Old Age and Loss of Capacity?
A natural consequence of battery use is that the active materials of the plates slowly disintegrate. In course of time, the remaining active material lowers the capacity of the battery until it is unable to do its job properly. A battery that has lost the capacity to the extent of 70 percent or more of the original capacity has ceased to be capable of giving good starting service.
What Is the Common Cause of Battery Terminal Corrosion?
Corrosion that may form on battery terminals, cable ends, carriers and adjoining metal parts must be cleaned off. If it accumulates it will cause high resistance at the battery terminals and result in serious starting trouble.
Acid Spilling-What Is the Main Cause of Acid Loss of a Battery?
The main cause of acid loss is overcharging which causes acid to spill from the battery in the form of moisture or may be carried away from the cells in a fine mist. This causes excessive corrosion leading to the troubles already outlined.
Mechanical Troubles.
Batteries in service on the vehicle are subject to considerable vibration with the risk of mechanical troubles developing. It is important that the battery condition and its mounting in the vehicle are checked regularly.
What Does Excessive Load on Battery Mean?
If too big a load is placed on the battery, or if a replacement battery too low in capacity is fitted, the battery will become discharged and the results described under “undercharging” will result.
Why Do We Need Battery Hold Down Clamps and Bolts?
Batteries must be securely fitted in the vehicle, otherwise, excessive vibration can cause the mechanical troubles previously detailed.
Why Is It Important to Keep Batteries and Cable Connections Clean?
Battery cables must be of adequate capacity and in good condition with all connections clean and tight. The cables and connections carry the full starter current which may be several hundreds of amperes and unless they are of proper size, in good condition, and properly and tightly connected, starting trouble will inevitably develop.
Sometimes battery cables are replaced with new cables of inadequate size. This increases the resistance of the cable and lowers the voltage at the starter, causing starting difficulties.
What Are the Problems of Battery System?
A battery that has been overcharged will use too much water, may gas excessively, corrode rapidly, and develop electrical leakage. The cure is to reduce the charging rate.
A battery that has been undercharged will become sulfated. Sulphation occurs also where batteries are left standing too long in a discharged condition or are operated too long in a partially discharged state. Undercharging causes low battery capacity, hard starting, and freezing of the electrolyte in extreme temperatures. The cure is to increase the charging rate.
Overfilling batteries may cause the battery to boil over and gas excessively with loss of electrolyte, possible excessive corrosion, and internal short circuits. The correction is to keep the battery properly topped up in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions.
Underfilling batteries leave the top of the separators and plates exposed and can cause plate shedding, charred separators, under capacity, and hard starting. The correction is periodic battery inspection and topping up.
Improper installation of batteries will cause mechanical troubles and also lead to loss of electrolytes, excessive corrosion and electrical leakage. The correction is to check the installation and make sure it is efficient.
What Is the Easiest Way to Test a Battery?
Battery inspection and testing should be carried out as a regular routine process. It is not something to be done only when the customer experiences actual trouble. Modern instruments and methods are now available which make it as easy to test batteries as the pressure of a tire.
If batteries were tested as regularly as tire pressures are checked, car owners would derive considerable benefit in improved starting performance and longer battery life. Correspondingly, the service station would derive considerable benefit through higher sales of battery charging and new batteries, and also from additional services such as voltage regulator testing and adjustment, new battery cables, and new fan belts.
What Are the Basic Battery Tests?
Three tests are needed to determine the condition and serviceability of a battery.
(i) Battery mechanical condition.
(ii) State of charge of all cells.
(iii) Battery capacity and condition.
The inspections required to determine battery mechanical condition are:
Terminals and Cables.
Remove both terminals and check for corrosion and cable condition, paying particular attention to the underside of the terminal clamps.
Terminal Posts.
Check for corrosion, hard or burned surfaces and also check for looseness in the lids and signs of distortion.
Stoppers.
Check the rubber sealing ring and the condition of the screw thread; see that the vents are clear and that gas relief valves, where fitted, are free and working correctly.
Lids and Sealing.
See that all lids are properly amalgamated with the sealing material and are not cracked or chipped. There must be no film of wet or dirty deposit on the lid surfaces.
Inter-cell Links.
Check that these are properly burned on by gently prising under each link with an old screwdriver.
Case.
Check for cracks around the top edges of the battery container and inspect the holding nuts, rods and end lugs. See that the battery is firmly mounted with no rubbing against the cradle or box. If there is any white corrosion on adjoining metalwork, this indicates a possible leaky case and a special check should be made.
Electrolyte.
See that the electrolyte level is also about {1 above the level of the separators}.
Testing Battery State of charge.
Two methods are available for testing the battery state of charge:
(i) Testing cell-specific gravity with a hydrometer.
(ii) Testing cell open-circuit voltages with an open-circuit test Voltmeter.
Both methods give a fairly accurate indication of the electrical state of charge of all cells and they also indicate the general condition of the battery by showing the extent to which cell readings are uniform.
How to Use Hydrometer for Battery Testing?
By using a good quality hydrometer, sufficient electrolyte is withdrawn from the cells and the specific gravity of each is carefully noted. All cells should give readings uniform within 25 points. If readings are not uniform within 25 points it indicates a possibly defective battery The battery should be recharged and a further test then made.
When making a hydrometer test, siphon the proper amount of electrolyte and hold the hydrometer so that the eye is on a level with the surface of the liquid in the barrel. Keep the float vertical and place a finger over the tip of the tube to avoid acid spilling. After testing, return the electrolyte to the same cell from which it was removed. Keep the tube clean to prevent the float from sticking to the side of the tube.
Where battery electrolyte level is low it may not be possible to siphon a sufficient amount of electrolyte to make a hydrometer test. Water must therefore be added and the battery should then be charged so that the electrolyte and water are thoroughly mixed before a hydrometer test is made.
When hydrometer tests are made at high or low temperatures, readings should be compensated by adding four points for every ten degrees by which the temperature exceeds the manufacturer’s standard and by deducting four points for every ten degrees by which the temperature is lower than the manufacturer’s standard. (The average standard is 60°F.)
What Is Open Circuit Voltage Testing?
This method of testing gives results comparable to hydrometer testing without the inconvenience of siphoning acid, interpreting specific gravity readings in terms of state-of-charge and making temperature corrections.
The principle of open-circuit voltage testing is based upon the fact that there is a definite relationship between the open-circuit voltage of the cell and the specific gravity. This relationship is shown in (Fig. 7.1). The approximate equivalent between the meter reading, open-circuit cell voltage and specific gravity is as follows.
| Meter Reading | Voltage | Approx. Specific Gravity |
| 10 15 18 20 22 24 26 28 | 1.98 2:03 2:06 2.08 2:10 2.12 2.14 2.16 | 1.120 1.180 1.210 1.220 1.260 1.280 1.300 1.325 |
The test instrument comprises a portable voltmeter with a voltage scale from 1.85 to 2.25 divided into forty divisions, each of 0:01V. Some instruments have two scales; one for use where batteries are tested after fast charging when the temperature of the electrolyte is relatively high and the other for use after slow charging when the electrolyte temperature is lower.
To make the test, the meter prods are pressed firmly on the cell terminals, with the red prod point to the positive and the black prod point to the negative cell terminal. When contact is made, the meter needle will move slightly to the left against a stop and then swing up on the scale and indicate the cell condition. Care must be taken to prod only one cell at a time, particularly when testing 12V batteries
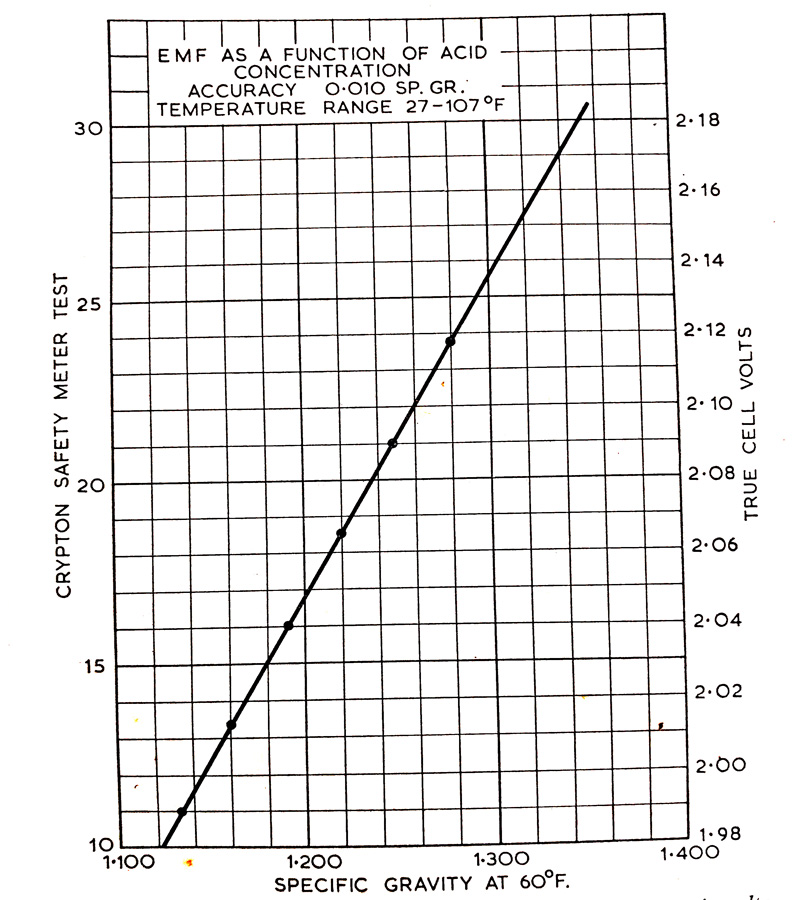
Fig. 7.1. Relation between meter reading, battery open-circuit volts and specific gravity.
Where there is a sealing compound over the connectors. Contact may be made at any point on the cell strap; it is not necessary to make contact exactly where the cell terminal connects to the strap.
If the vehicle engine has been running previous to the test, all lights, radio and heater should be turned on for about one minute before the test is made to remove the surface charge on the battery plates.
If all cell readings vary less than six scale divisions and are in the “ Serviceable” zone, the battery is in good condition.
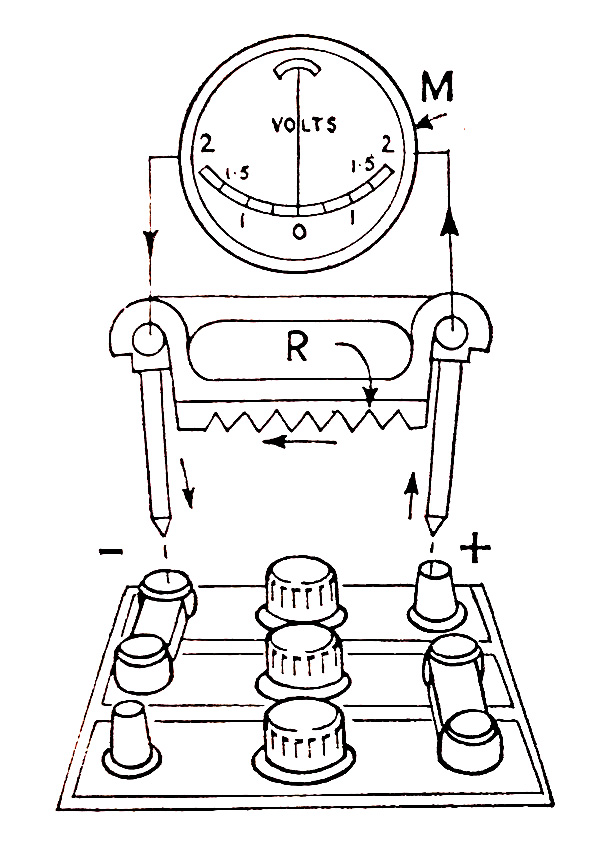
Fig. 7.2. Testing battery with heavy discharge tester.
If the cell readings vary less than six scale divisions and any one or more cells read in the “ Recharge ” zone the battery needs recharging to avoid starting failure. If any two readings vary by six scale divisions or more, the battery may be nearing the end of its useful life and should be recharged and retested. (Fig. 7.3) shows typical meter test indications.
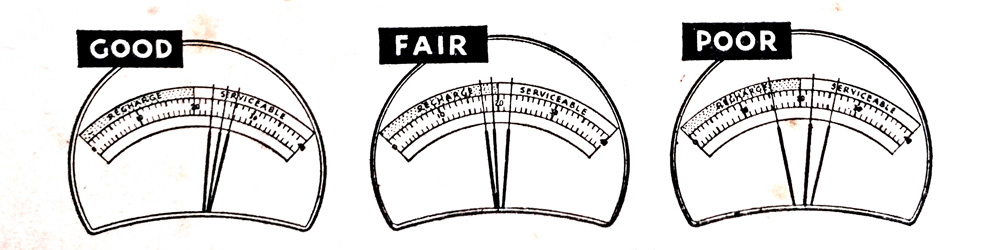
Fig. 7.3. Typical meter test indications of battery cell readings.
How To Test Battery Starting Capacity?
The principle used to test the starting capacity of a battery is to measure the voltage of each cell whilst a current comparable to the heavy current used for starting the engine is taken from the battery.
Three methods are available.
(i) A direct test of the battery voltage, using the starter as a load.
(ii) Testing cell capacity with a heavy discharge cell tester.
(iii) Testing cell voltage with a measured and applied variable load.
To test battery capacity using the starter as a load, an accurate cell test voltmeter is connected to each battery cell in turn and the voltage is noted while the starter is turned. All cells should read not less than 1.5V and be uniform within 0:01 V.
To make a heavy discharge cell test, a portable voltmeter with a built-in loading resistance is used. When the instrument prods are connected across the positive and negative terminals of a battery, current flows through this resistance and the voltmeter reads the cell voltage while the current is flowing. The average value of the current is 150A which approximates the normal average starting load in service. The tester is connected to each cell in turn and the voltage of any cell should not be less than 1.5V and should remain constant for at least ten seconds. If the cell voltage is lower than 1.5V or falls away rapidly during the ten seconds, it indicates that the cell has too low a capacity for good starting service.
A heavy-discharge test should not be made unless the battery has been previously tested for the state of charge. The reason is that if the test is made on a battery-less than 75 percent charged it will give misleading results. When made on a battery more than 75 percent charged, the test will indicate the possibility of worn-out plates, sulphation, clogged or defective separators and cell failure. If, however, the battery is less than 75 percent charged, the test is not conclusive.
A disadvantage of the heavy-discharge method of cell testing is the fact that only one load is applied to the cell. Strictly, therefore, the method is suitable for only one capacity of the battery, that for which the instrument load is suitable. When tests are made on a smaller capacity battery the load will be too severe and batteries may be passed as deficient when they are satisfactory. If the test is made on a larger battery than that for which the instrument load is calibrated, the test will not be severe enough and the battery may be passed as in good condition whereas it may be deficient. This condition can, to some extent, be compensated for by varying the time for which the tester is applied, reducing the time slightly for smaller batteries and increasing it for larger batteries.
How Is Variable-Discharge Capacity Tested?
This is a superior method of testing battery capacity because it enables the correct load to be selected for the battery being tested.
The equipment comprises a moving-coil ammeter (reading up to 500A), moving-coil voltmeter (reading up to 2:5V) and a variable carbon pile rheostat designed for discharge loads up to about 400A.
The carbon pile rheostat is adjusted until the meter reads a current value equal to twice the ampere-hour rating of a 6V battery, or three times the ampere-hour rating of a 12V battery. The load is read on The rating of a 12V” Then the ammeter and is applied for 15 seconds when the voltmeter reading should not be less than 1.5V for single cells, 4.5V for a 6V battery and 9V for a 12V battery. If the battery voltages are within these limits, It can be considered suitable for continued service. If, however, the voltage is lower the battery is suspect and the cause of low capacity should be investigated.
How To Test Battery Condition and Health?
One of the biggest problems experienced in servicing batteries is to determine quickly what is needed to restore full battery performance. When a starter load test or heavy-discharge test shows that battery capacity is low, the battery may be discharged and require normal charging or maybe sulfated and need special slow-rate charging or maybe worn out and require replacement.
A comparatively new method of testing batteries provides a satisfactory answer to these three possibilities. The test is made with a battery capacity tester and fast charger, available either as an individual or combined unit.
The battery is first tested with a variable-discharge capacity tester as described in the preceding paragraph. If the test shows that the battery voltage is lower than 4.5V for a 6V battery or 9V for a 12V battery the test is continued, using a fast battery charger.
The battery is put on fast charge for three minutes at a charging rate of 75A for 6V batteries or 40A for 12V batteries. At the end of the three minutes, and with the charging current still flowing, the individual cell voltages are tested. They must all be within 0.1V. If they are not, the battery is defective and must be replaced.
If the cells are even within 0:1V, the total battery voltage is tested with the battery still being fast-charged. If the voltage is less than 7.75V for a 6V battery or less than 15.5V for a 12V battery, the battery is discharged and will satisfactorily take a fast charge.
If, however, the voltage rises above 7.75V for a 6V battery or 15.5V for a 12V battery, after three minutes of fast charge, the battery is probably sulfated and not suitable for satisfactory service. It should either be replaced with a new battery, or a rental battery fitted and the vehicle battery put on a continuous slow charge to see if the sulphation can be broken down and battery condition restored.
How To Test Battery Temperature Sensor?
Typically what happens when winter comes if your battery is a bit weak. Your vehicle’s not going to start to change this battery out and look at the temperature sensor for the battery. Let’s show you how to test one of these battery temperature sensors.

The black should be in its common slot and redone is positive slot.

If you look on your meter it should show any indication of what it’s all for, there’s a little ohm sign on there.
So that’s the positions that you want and that’s the setting that you want now.
Now when you’re testing this, if you’re using multimeters there’s an ohm setting and set that to 20k or 200k. If you’re not on the right setting nothing will show up on the display. It might exceed whatever the decimal places are so you won’t see anything. If nothing’s showing up make sure you have the right setting on there that’s been showing up in the number field.

Do this before they warm up just to see if it shows the correct number. The multimeter will show around 65 Ohm for high temperatures.

Let’s use a hairdryer. When it’s warming up the number goes lower meaning the resistance is going down and it’s doing what it’s supposed to do.
If the sensor is fine, so don’t need to replace the temperature sensor for the battery.
What’s the big deal about having this temperature sensor for the battery. It tells the system however it does it through the resistance. It sends a signal and it says hey we need to put more power into that battery to get it charged up properly. Because of a bull cold battery, the current doesn’t like to flow very well. So it pushes some more power into there to get things moving.
Also if it’s really hot it knows to slow down the charging system. So that you don’t overheat the battery and wreck it.
If everything’s working properly that’s what this is all about. If you want your battery to last a long time you should check this sensor to see if it’s working or not.
In short about battery sensor testing.
- Set multimeter to ohm 20k or 200k.
- Use multimeter black should be in its a common slot and redone is another positive slot (Where Ohm sign).
- Hold multimeter positive and negative probe lead with sensor’s wire.
- Make sure the sensor gives you a high-temperature reading around 65 or high ohm.
- Measure low-temperature reading using a hairdryer blow hot air on the sensor, the meter will show a low number like 20 or 18 Ohm.
- If the multimeter shows both high and low indications that means the sensor is good.
- Also if you need to know that the sensor gives you the proper reading use another new or good sensor.
Innova Multimeter 3320 Car Battery Test.
- Set multimeter 12 DC volt.
- Put red jack into Ohm sign slot.
- Black should be in its common slot.
- Do not put any jack in (DC10A) this slot while testing, which might damage your multimeter.
- Now hold the red lead on positive and black lead on the negative battery post.
- The battery needs to be at least 12.2volt or higher to start the engine.
- If it’s lower than 12.2volt battery needs to recharge.
Battery Testing With Multimeter.
Battery Voltage Test.
- Mltimeter: Multimeter set DCV 20.
- Put red jack into Ohm sign slot and Black should be in its a common slot.
- Meter lead(+) to battery(+)terminal and meter lead(-) to battery(-)terminal.
- Voltage must be 12.2volt or higher. If less, then charge your battery.
Battery Load Test.
- Multimeter: Multimeter set DCV 20.
- Put red jack into Ohm sign slot and Black should be in its a common slot.
- Meter lead(+) to battery(+)terminal and Meter lead(-) to battery(-)terminal > Start engine.
- Engine starting time, If the minimum volt is 9.6volt, then the battery is ok. But if it’s below the 9.6volt then the battery needs to recharge.
You can use a battery load tester instead of a multimeter. Also, different multimeters have different functions. Before the battery load test needs to make sure that your multimeter is compatible with the load test.
Voltage and Charge Status Chart.
| Battery Voltage | Battery Charge Status |
| While Engine Running: 13.7 to 14.7 volt | Good |
| When Engine Off | Battery Charge Status |
| 12.6V: fully Charged | 100% Charged-Good |
| 12.4V: 75% Charge | 75% Charged-Good |
| 12.2V: 50% Charge | 50% Charged – Needs Charge |
| 12V: 25% Charge | 25% Charged – Needs Charge |
| 11.9V and below: effectively zero charge | Battery Discharged. |
How To Test A Battery For A Dead Cell?
When a battery completely charges but won’t perform perfectly, that means a cell goes dead. Once a cell goes dead, the battery is bad and needs to be replaced. The 12-volt batteries used in automobiles contain six separate cells, each cell has 2-volt. The best test is to check the specific gravity of the electrolyte fluid of an auto battery for a dead cell. Specific gravity is the viscosity of the electrolyte fluid compared to water. The specific gravity for the electrolyte is perfectly1.265. A low specific gravity in one cell compared to other cells means it’s dead. When batteries are flooded, it is easy to determine the battery for physical damage.
Can a dead cell in a car battery be fixed?
Well, the good news is, that a dead battery or a dead cell in a battery is repairable. You need not think of buying a new battery in an emergency as there are ways to save the existing battery.
How would you know if your battery or one of the cells is going to be dead soon?
As it is known that the usual car battery is composed of six cells and is 12 Volts. Voltage and amperage produced in the battery chemically are what ignites the car.
How to revive a dead battery cell?
The battery is what runs the vehicles. A faulty or weak cell can be repaired by restoring the chemical balance of the battery.
How do you tell if a car battery has a dead cell?
Sulphation causes permanent damage sometimes. But if permanent damage has not been done, then restoring a weak cell battery is easy.
Preparations for revival.
Clean the cells so that you have access to all the cells. Do so by removing all loose dirt and oil from the top of the battery with a clean dry cloth.
Check the cells.
To check the depth of electrolyte in each cell, flash a flashlight into each cell and note the depth.
Add the acid.
After checking, if the cell is faulty, remove the caps again and wear the safety equipment again. After replacing the faulty cell pour acid carefully.
Check The Battery Cell Using A Hydrometer.
Safety first works last.
Work in a well-ventilated area and wear rubber gloves and safety glasses. Keep the battery away from open flames. Car batteries contain sulfuric acid, which can harmful to the eyes and skin.
Let’s start the test.
Disconnect the battery lines using a crescent wrench, starting with the negative battery terminal ( marked with a minus sign). Connect the battery to a battery charger and allow it to charge to capacity. Use a three-phase battery charger for the best results, which is designed for lead-acid batteries. After complete charging, disconnect the leads to the battery charger. Then the plastic caps off the top of the battery. Insert the rubber tube of a battery testing hydrometer into a battery cell.

A cell is fully charged.
- As the (Potential of Hydrogen)Ph scale has risen up to the green point. Which indicates that the cell is maximum charged.
- When scale has risen up to the white then it’s a minimum charge.
- When the scale has risen up to the red then it’s a dead cell.
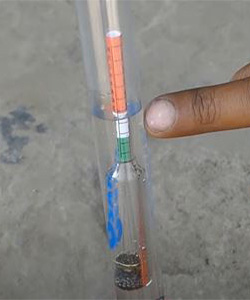
A cell is a minimum level charged.
When the scale has risen up to the white then it’s a minimum charge. A cell charge and PH scale color could be different.

A cell is dead.
Flot did not rise to an even point. A cell is not able to store any charge in the future.
Repeat the specific gravity test for each cell of the battery. Compare the readings. If only one cell of a battery is dead, the battery needs to be replaced. Because the battery can’t make up the required voltage.
For example: If the battery is 12 volt then it has 6 cells. If one cell is dead it can’t make up the required 12 volts.
How To Replace A Dead Cell In A Car Battery?
- Use safety first.
- Remove battery caps, water/acid.
- Use a hacksaw blade to cut upper the cover of the battery.
- Use a hammer and punch to remove the cutting piece.
- Remove old dead cell then wash the battery with water.
- Put a new cell into the battery.
- Then joint the cutting piece with the battery and pour water/acid then tighten the cap.